#代码 import os import sys from collections import namedtuple from PIL import Image class Nude(object): Skin = namedtuple("Skin", "id skin region x y") def __init__(self, path_or_image): # 若 path_or_image 为 Image.Image 类型的实例,直接赋值 if isinstance(path_or_image, Image.Image): self.image = path_or_image # 若 path_or_image 为 str 类型的实例,打开图片 elif isinstance(path_or_image, str): self.image = Image.open(path_or_image) # 获得图片所有颜色通道 bands = self.image.getbands() # 判断是否为单通道图片(也即灰度图),是则将灰度图转换为 RGB 图 if len(bands) == 1: # 新建相同大小的 RGB 图像 new_img = Image.new("RGB", self.image.size) # 拷贝灰度图 self.image 到 RGB图 new_img.paste (PIL 自动进行颜色通道转换) new_img.paste(self.image) f = self.image.filename # 替换 self.image self.image = new_img self.image.filename = f # 存储对应图像所有像素的全部 Skin 对象 self.skin_map = [] # 检测到的皮肤区域,元素的索引即为皮肤区域号,元素都是包含一些 Skin 对象的列表 self.detected_regions = [] # 元素都是包含一些 int 对象(区域号)的列表 # 这些元素中的区域号代表的区域都是待合并的区域 self.merge_regions = [] # 整合后的皮肤区域,元素的索引即为皮肤区域号,元素都是包含一些 Skin 对象的列表 self.skin_regions = [] # 最近合并的两个皮肤区域的区域号,初始化为 -1 self.last_from, self.last_to = -1, -1 # 色情图像判断结果 self.result = None # 处理得到的信息 self.message = None # 图像宽高 self.width, self.height = self.image.size # 图像总像素 self.total_pixels = self.width * self.height def resize(self, maxwidth=1000, maxheight=1000): """ 基于最大宽高按比例重设图片大小, 注意:这可能影响检测算法的结果 如果没有变化返回 0 原宽度大于 maxwidth 返回 1 原高度大于 maxheight 返回 2 原宽高大于 maxwidth, maxheight 返回 3 maxwidth - 图片最大宽度 maxheight - 图片最大高度 传递参数时都可以设置为 False 来忽略 """ # 存储返回值 ret = 0 if maxwidth: if self.width > maxwidth: wpercent = (maxwidth / self.width) hsize = int((self.height * wpercent)) fname = self.image.filename # Image.LANCZOS 是重采样滤波器,用于抗锯齿 self.image = self.image.resize((maxwidth, hsize), Image.LANCZOS) self.image.filename = fname self.width, self.height = self.image.size self.total_pixels = self.width * self.height ret += 1 if maxheight: if self.height > maxheight: hpercent = (maxheight / float(self.height)) wsize = int((float(self.width) * float(hpercent))) fname = self.image.filename self.image = self.image.resize((wsize, maxheight), Image.LANCZOS) self.image.filename = fname self.width, self.height = self.image.size self.total_pixels = self.width * self.height ret += 2 return ret # 分析函数 def parse(self): # 如果已有结果,返回本对象 if self.result is not None: return self # 获得图片所有像素数据 pixels = self.image.load() # 遍历每个像素 for y in range(self.height): for x in range(self.width): # 得到像素的 RGB 三个通道的值 # [x, y] 是 [(x,y)] 的简便写法 r = pixels[x, y][0] # red g = pixels[x, y][1] # green b = pixels[x, y][2] # blue # 判断当前像素是否为肤色像素 isSkin = True if self._classify_skin(r, g, b) else False # 给每个像素分配唯一 id 值(1, 2, 3...height*width) # 注意 x, y 的值从零开始 _id = x + y * self.width + 1 # 为每个像素创建一个对应的 Skin 对象,并添加到 self.skin_map 中 self.skin_map.append(self.Skin(_id, isSkin, None, x, y)) # 若当前像素不为肤色像素,跳过此次循环 if not isSkin: continue # 设左上角为原点,相邻像素为符号 *,当前像素为符号 ^,那么相互位置关系通常如下图 # *** # *^ # 存有相邻像素索引的列表,存放顺序为由大到小,顺序改变有影响 # 注意 _id 是从 1 开始的,对应的索引则是 _id-1 check_indexes = [_id - 2, # 当前像素左方的像素 _id - self.width - 2, # 当前像素左上方的像素 _id - self.width - 1, # 当前像素的上方的像素 _id - self.width] # 当前像素右上方的像素 # 用来记录相邻像素中肤色像素所在的区域号,初始化为 -1 region = -1 # 遍历每一个相邻像素的索引 for index in check_indexes: # 尝试索引相邻像素的 Skin 对象,没有则跳出循环 try: self.skin_map[index] except IndexError: break # 相邻像素若为肤色像素: if self.skin_map[index].skin: # 若相邻像素与当前像素的 region 均为有效值,且二者不同,且尚未添加相同的合并任务 if (self.skin_map[index].region != None and region != None and region != -1 and self.skin_map[index].region != region and self.last_from != region and self.last_to != self.skin_map[index].region) : # 那么这添加这两个区域的合并任务 self._add_merge(region, self.skin_map[index].region) # 记录此相邻像素所在的区域号 region = self.skin_map[index].region # 遍历完所有相邻像素后,若 region 仍等于 -1,说明所有相邻像素都不是肤色像素 if region == -1: # 更改属性为新的区域号,注意元祖是不可变类型,不能直接更改属性 _skin = self.skin_map[_id - 1]._replace(region=len(self.detected_regions)) self.skin_map[_id - 1] = _skin # 将此肤色像素所在区域创建为新区域 self.detected_regions.append([self.skin_map[_id - 1]]) # region 不等于 -1 的同时不等于 None,说明有区域号为有效值的相邻肤色像素 elif region != None: # 将此像素的区域号更改为与相邻像素相同 _skin = self.skin_map[_id - 1]._replace(region=region) self.skin_map[_id - 1] = _skin # 向这个区域的像素列表中添加此像素 self.detected_regions[region].append(self.skin_map[_id - 1]) # 完成所有区域合并任务,合并整理后的区域存储到 self.skin_regions self._merge(self.detected_regions, self.merge_regions) # 分析皮肤区域,得到判定结果 self._analyse_regions() return self # self.merge_regions 的元素都是包含一些 int 对象(区域号)的列表 # self.merge_regions 的元素中的区域号代表的区域都是待合并的区域 # 这个方法便是将两个待合并的区域号添加到 self.merge_regions 中 def _add_merge(self, _from, _to): # 两个区域号赋值给类属性 self.last_from = _from self.last_to = _to # 记录 self.merge_regions 的某个索引值,初始化为 -1 from_index = -1 # 记录 self.merge_regions 的某个索引值,初始化为 -1 to_index = -1 # 遍历每个 self.merge_regions 的元素 for index, region in enumerate(self.merge_regions): # 遍历元素中的每个区域号 for r_index in region: if r_index == _from: from_index = index if r_index == _to: to_index = index # 若两个区域号都存在于 self.merge_regions 中 if from_index != -1 and to_index != -1: # 如果这两个区域号分别存在于两个列表中 # 那么合并这两个列表 if from_index != to_index: self.merge_regions[from_index].extend(self.merge_regions[to_index]) del(self.merge_regions[to_index]) return # 若两个区域号都不存在于 self.merge_regions 中 if from_index == -1 and to_index == -1: # 创建新的区域号列表 self.merge_regions.append([_from, _to]) return # 若两个区域号中有一个存在于 self.merge_regions 中 if from_index != -1 and to_index == -1: # 将不存在于 self.merge_regions 中的那个区域号 # 添加到另一个区域号所在的列表 self.merge_regions[from_index].append(_to) return # 若两个待合并的区域号中有一个存在于 self.merge_regions 中 if from_index == -1 and to_index != -1: # 将不存在于 self.merge_regions 中的那个区域号 # 添加到另一个区域号所在的列表 self.merge_regions[to_index].append(_from) return # 合并该合并的皮肤区域 def _merge(self, detected_regions, merge_regions): # 新建列表 new_detected_regions # 其元素将是包含一些代表像素的 Skin 对象的列表 # new_detected_regions 的元素即代表皮肤区域,元素索引为区域号 new_detected_regions = [] # 将 merge_regions 中的元素中的区域号代表的所有区域合并 for index, region in enumerate(merge_regions): try: new_detected_regions[index] except IndexError: new_detected_regions.append([]) for r_index in region: new_detected_regions[index].extend(detected_regions[r_index]) detected_regions[r_index] = [] # 添加剩下的其余皮肤区域到 new_detected_regions for region in detected_regions: if len(region) > 0: new_detected_regions.append(region) # 清理 new_detected_regions self._clear_regions(new_detected_regions) # 皮肤区域清理函数 # 只保存像素数大于指定数量的皮肤区域 def _clear_regions(self, detected_regions): for region in detected_regions: if len(region) > 30: self.skin_regions.append(region) # 分析区域 def _analyse_regions(self): # 如果皮肤区域小于 3 个,不是色情 if len(self.skin_regions) < 3: self.message = "Less than 3 skin regions ({_skin_regions_size})".format( _skin_regions_size=len(self.skin_regions)) self.result = False return self.result # 为皮肤区域排序 self.skin_regions = sorted(self.skin_regions, key=lambda s: len(s), reverse=True) # 计算皮肤总像素数 total_skin = float(sum([len(skin_region) for skin_region in self.skin_regions])) # 如果皮肤区域与整个图像的比值小于 15%,那么不是色情图片 if total_skin / self.total_pixels * 100 < 15: self.message = "Total skin percentage lower than 15 ({:.2f})".format(total_skin / self.total_pixels * 100) self.result = False return self.result # 如果最大皮肤区域小于总皮肤面积的 45%,不是色情图片 if len(self.skin_regions[0]) / total_skin * 100 < 45: self.message = "The biggest region contains less than 45 ({:.2f})".format(len(self.skin_regions[0]) / total_skin * 100) self.result = False return self.result # 皮肤区域数量超过 60个,不是色情图片 if len(self.skin_regions) > 60: self.message = "More than 60 skin regions ({})".format(len(self.skin_regions)) self.result = False return self.result # 其它情况为色情图片 self.message = "Nude!!" self.result = True return self.result # 基于像素的肤色检测技术 def _classify_skin(self, r, g, b): # 根据RGB值判定 rgb_classifier = r > 95 and \ g > 40 and g < 100 and \ b > 20 and \ max([r, g, b]) - min([r, g, b]) > 15 and \ abs(r - g) > 15 and \ r > g and \ r > b # 根据处理后的 RGB 值判定 nr, ng, nb = self._to_normalized(r, g, b) norm_rgb_classifier = nr / ng > 1.185 and \ float(r * b) / ((r + g + b) ** 2) > 0.107 and \ float(r * g) / ((r + g + b) ** 2) > 0.112 # HSV 颜色模式下的判定 h, s, v = self._to_hsv(r, g, b) hsv_classifier = h > 0 and \ h < 35 and \ s > 0.23 and \ s < 0.68 # YCbCr 颜色模式下的判定 y, cb, cr = self._to_ycbcr(r, g, b) ycbcr_classifier = 97.5 <= cb <= 142.5 and 134 <= cr <= 176 # 效果不是很好,还需改公式 # return rgb_classifier or norm_rgb_classifier or hsv_classifier or ycbcr_classifier return ycbcr_classifier def _to_normalized(self, r, g, b): if r == 0: r = 0.0001 if g == 0: g = 0.0001 if b == 0: b = 0.0001 _sum = float(r + g + b) return [r / _sum, g / _sum, b / _sum] def _to_ycbcr(self, r, g, b): # 公式来源: # http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19459831/rgb-to-ycbcr-conversion-problems y = .299*r + .587*g + .114*b cb = 128 - 0.168736*r - 0.331364*g + 0.5*b cr = 128 + 0.5*r - 0.418688*g - 0.081312*b return y, cb, cr def _to_hsv(self, r, g, b): h = 0 _sum = float(r + g + b) _max = float(max([r, g, b])) _min = float(min([r, g, b])) diff = float(_max - _min) if _sum == 0: _sum = 0.0001 if _max == r: if diff == 0: h = sys.maxsize else: h = (g - b) / diff elif _max == g: h = 2 + ((g - r) / diff) else: h = 4 + ((r - g) / diff) h *= 60 if h < 0: h += 360 return [h, 1.0 - (3.0 * (_min / _sum)), (1.0 / 3.0) * _max] def inspect(self): _image = '{} {} {}×{}'.format(self.image.filename, self.image.format, self.width, self.height) return "{_image}: result={_result} message='{_message}'".format(_image=_image, _result=self.result, _message=self.message) # 将在源文件目录生成图片文件,将皮肤区域可视化 def showSkinRegions(self): # 未得出结果时方法返回 if self.result is None: return # 皮肤像素的 ID 的集合 skinIdSet = set() # 将原图做一份拷贝 simage = self.image # 加载数据 simageData = simage.load() # 将皮肤像素的 id 存入 skinIdSet for sr in self.skin_regions: for pixel in sr: skinIdSet.add(pixel.id) # 将图像中的皮肤像素设为白色,其余设为黑色 for pixel in self.skin_map: if pixel.id not in skinIdSet: simageData[pixel.x, pixel.y] = 0, 0, 0 else: simageData[pixel.x, pixel.y] = 255, 255, 255 # 源文件绝对路径 filePath = os.path.abspath(self.image.filename) # 源文件所在目录 fileDirectory = os.path.dirname(filePath) + '/' # 源文件的完整文件名 fileFullName = os.path.basename(filePath) # 分离源文件的完整文件名得到文件名和扩展名 fileName, fileExtName = os.path.splitext(fileFullName) # 保存图片 simage.save('{}{}_{}{}'.format(fileDirectory, fileName,'Nude' if self.result else 'Normal', fileExtName)) if __name__ == "__main__": import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Detect nudity in images.') parser.add_argument('files', metavar='image', nargs='+', help='Images you wish to test') parser.add_argument('-r', '--resize', action='store_true', help='Reduce image size to increase speed of scanning') parser.add_argument('-v', '--visualization', action='store_true', help='Generating areas of skin image') args = parser.parse_args() for fname in args.files: if os.path.isfile(fname): n = Nude(fname) if args.resize: n.resize(maxheight=800, maxwidth=600) n.parse() if args.visualization: n.showSkinRegions() print(n.result, n.inspect()) else: print(fname, "is not a file")
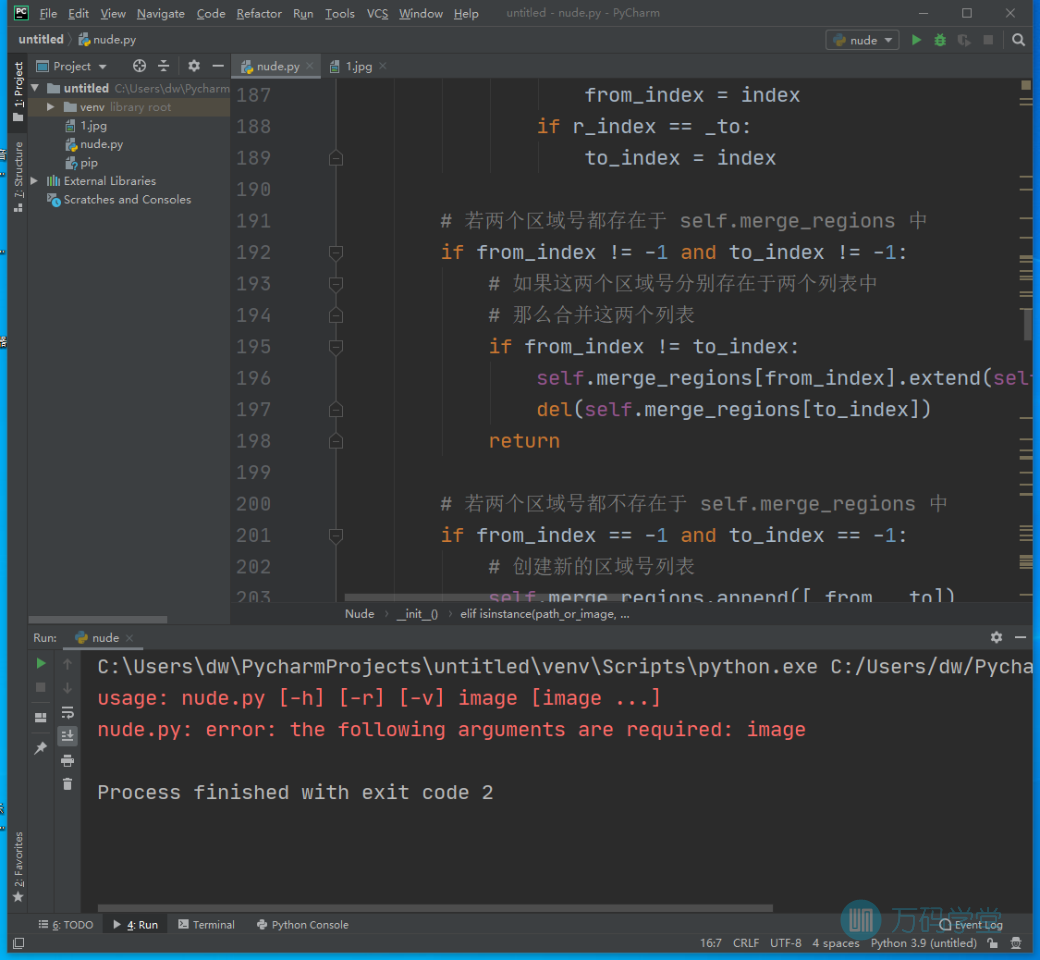
错误
这个程序运行需要参数来传递图片文件,你运行的时候没有传递,所以打印错误提示。
你可以修改一下程序,要不运行输入图片路径,要不干脆写死程序中绝对图片路径,测试程序。

0条评论
我要评论